Now Reading: A guide to regional differences within global university rankings.
-
01
A guide to regional differences within global university rankings.
A guide to regional differences within global university rankings.
In an increasingly interconnected world, where knowledge transcends borders and ideas are exchanged at lightning speed, the pursuit of educational excellence remains a paramount goal for institutions across the globe. Yet, as students, educators, and policymakers turn to university rankings as a beacon of quality, they often encounter a complex landscape marked by regional differences. From the ivy-covered walls of elite Western universities to the rapidly emerging institutions in Asia and beyond,these rankings tell varied narratives shaped by cultural,economic,and social contexts. In this article,we delve into the intricacies of regional variations within global university rankings,exploring how geographic nuances influence institutional performance and recognition. By unraveling the threads that bind and differentiate universities across continents, we aim to provide a extensive guide that not only informs but also encourages a deeper understanding of what it means to measure academic success in a diverse world.
Understanding the Landscape of Global University Rankings
The realm of global university rankings is incredibly diverse, shaped by various regional perspectives and academic cultures. Each region brings its own unique metrics and values, reflecting local priorities and educational philosophies. As an example, North American universities often emphasize research output and funding, whereas European institutions may focus more on teaching quality and student satisfaction. This disparity influences how universities are assessed globally, leading to variations in rankings that can create confusion for prospective students and academics alike.
To better understand these differences, consider the following key factors that contribute to regional rankings:
- Research Funding: Institutions in North America may excel due to significant financial resources.
- Teaching Methods: European universities often adopt holistic and innovative teaching practices.
- International Collaboration: asian universities are increasingly recognized for global partnerships and collaborative research.
- Local Relevance: Rankings can reflect how well universities address regional societal needs and economic challenges.
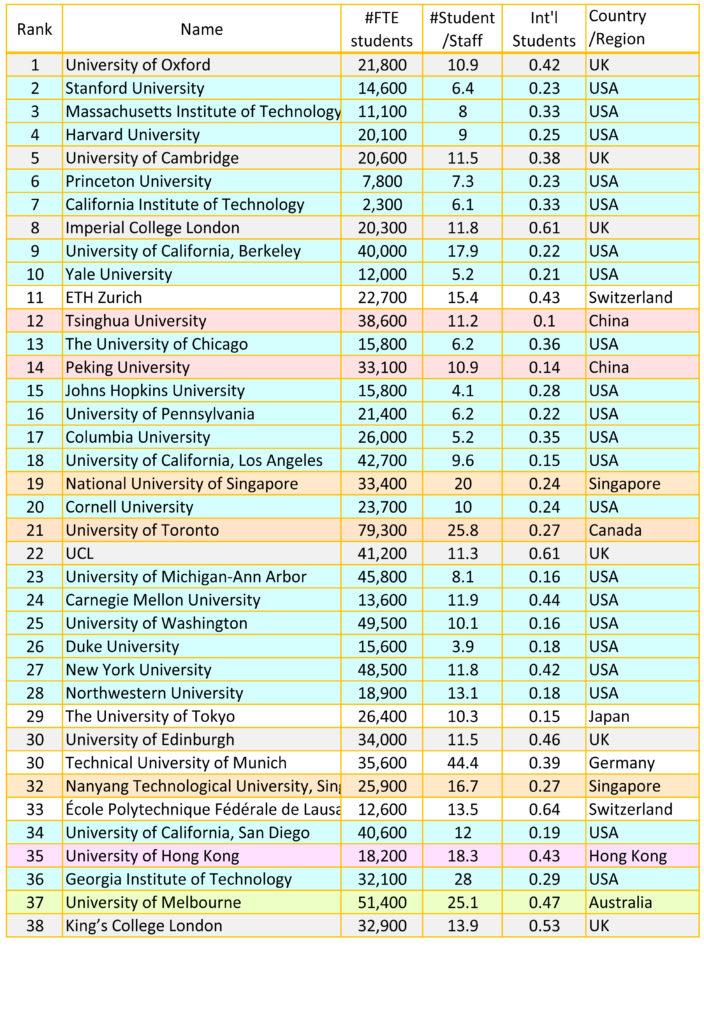
To illustrate these disparities, here’s a simplified comparison of average rankings for universities across different regions:
| Region | Average Research Score | Average Teaching Score | International Outlook Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 90% | 85% | 80% |
| Europe | 75% | 90% | 70% |
| Asia | 80% | 80% | 85% |
Exploring Regional Variations in Academic Evaluation Criteria
As universities seek to enhance their global standings, it becomes evident that academic evaluation criteria vary significantly across different regions. These criteria often reflect local educational philosophies, cultural values, and economic realities. As a notable example, in North America, a considerable emphasis is placed on research output and publication metrics, while in Europe, there is a more balanced approach that factors in teaching quality and student engagement.This divergence can influence not just university rankings but also the strategic focus universities adopt in their academic programs.
Furthermore, the criteria employed in regional rankings highlight particular strengths and aspirations within academic communities.Key aspects may include:
- Research Impact: many Asian universities invest heavily in research collaborations that foster global partnerships.
- Teaching Excellence: European institutions often prioritize mentorship and teaching methodologies over purely research-oriented metrics.
- Community Engagement: Institutions in Latin America frequently emphasize their roles within local communities, integrating social responsibility into their evaluation.
To better illustrate these differences, the table below outlines some of the moast notable regional focuses in academic evaluation:
| Region | Evaluation Focus |
|---|---|
| North America | Research Output and publication metrics |
| Europe | Teaching Quality and Student Engagement |
| Asia | Global Research Collaborations |
| Latin America | Social Responsibility and Community Engagement |
Unpacking the Influence of Cultural context on Rankings
The impact of cultural context on university rankings is multi-faceted, as different regions prioritize distinct values and educational outcomes. As an example, institutions in Western countries often emphasize research output and international collaboration, which reflects the globalized approach of their academic systems. In contrast, universities in Asian nations may focus more on rigorous examination standards and employability rates, driven by local job market demands. This divergence leads to a perception that not all rankings equally reflect the quality of education or the contributions of each institution. specific factors influenced by cultural context include:
- Research Funding: Varies significantly based on governmental and private investments, often influenced by national priorities.
- Student Engagement: Different regions have unique approaches to student involvement in campus life, which may influence outcomes and perceptions.
- Curriculum Relevance: Tailored to meet the cultural and economic needs of the region, affecting the ranking performance.
Furthermore, how universities are evaluated can also vary considerably depending on the cultural lens through which data is interpreted. While some rankings prioritize quantitative metrics,others may incorporate qualitative assessments that account for regional educational philosophies. A comparative look at rankings across diverse cultural contexts illustrates the complexity of educational ecosystems. The following table demonstrates how a few prominent educational rankings differ in their evaluation criteria by region:
| Ranking Organization | Region | Key Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| QS World University Rankings | Global | Academic Reputation, Employer Reputation, Research Quality |
| Times Higher Education | Global | Teaching, Research, International Outlook |
| Shanghai Ranking | global | Nobel Prizes, Field Medals, Highly Cited Researchers |
| Webometrics | Global | Web Visibility, Rich Files, Scholar |
Strategic Approaches for Institutions to Enhance their Standings
To elevate their positions in global university rankings, institutions should adopt a multifaceted approach that aligns with their unique regional characteristics.Understanding local dynamics is crucial; universities must tailor their strategies to address factors pertinent to their geographical and cultural contexts. This includes investing in community engagement initiatives that not only raise the university’s profile but also contribute meaningfully to local advancement. additionally, institutions should focus on establishing strong partnerships with local industries and governmental bodies, facilitating a reciprocal relationship that underscores the university’s relevance in the regional ecosystem.
Another pivotal strategy is the emphasis on international collaboration. By building ties with foreign institutions, universities can enhance their research output, thereby improving their standing in global metrics. Hosting joint research projects and facilitating student exchanges can significantly enrich educational quality and cultural diversity on campus. Furthermore, institutions should enhance their digital presence by leveraging online platforms to share achievements, research findings, and community contributions.This proactive communication approach catapults their visibility on international platforms, showcasing the institution’s comprehensive commitment to excellence across various domains.
The Conclusion
navigating the intricate landscape of global university rankings can feel like charting a course through uncharted waters. This guide has unveiled the myriad regional differences that shape these rankings, highlighting the unique strengths and challenges faced by institutions across the globe. From the distinct academic cultures in Europe and Asia to the burgeoning innovations in Africa and Latin America, it’s clear that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to higher education evaluation.
As prospective students, educators, and policymakers ponder the implications of these rankings, it’s crucial to consider the broader context of each institution’s achievements and aspirations. The diversity of academic excellence serves as a reminder that knowledge knows no borders; each region contributes its own narrative to the global discourse of education.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of regional differences empowers us to appreciate the rich tapestry of academia and the varied paths to success within it. By engaging with these complexities, we can foster a more informed dialogue about higher education and its vital role in shaping our world. So, whether you’re a scholar seeking your next adventure or an institution striving for recognition, take heart—there’s more than one way to measure greatness in the realm of knowledge.



























